Mitosis is how body cell duplicate, skin, muscle, neurons.
Meiosis is how sex cells duplicate, ova (egg), sperm.
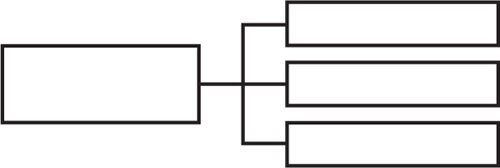
Cell division type
|
Mitosis
|
Meiosis
|
Function
|
Replicate body cells
skin, muscle, bone |
Replicate sex cells
ovum (egg), sperm |
Reproduction
|
Asexual
|
Sexual
|
Genetically
|
Identical
|
different
|
# of daughter cells
|
2 diploid cells
|
4 haploid cells
|
# of divisions
|
1
|
2
|
Chromosome #
|
46
|
23
|
Stages of Mitosis and Meiosis
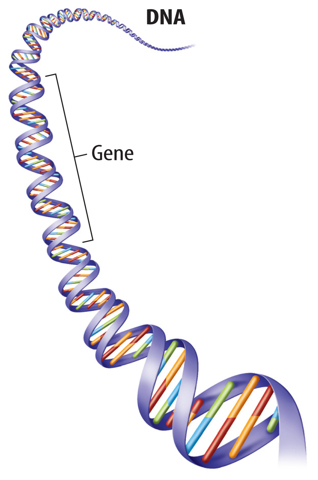
DNA molecules are double-stranded helices.
Heredity is how we pass these coded traits on to our children.
Homozygous are alleles of the same type, such as RR, rr.
Heterozygous are combinations with both a dominant and recessive allele, such as Bb.
A dominant (D) allele will be expressed or seen (in phenotype) if it is homozygous (RR) or if it
is heterozygous (Rr)
A recessive (r) allele is expressed (seen in phenotype) when it is paired (2) with another recessive
allele of the same type (such as LL, ll). It is masked when combined with a dominant allele (such
as in Ll).
Genotype - Genetic makeup
Homozygous Dominant
PP = Dominant color
Heterozygous
Pp = Dominant color
Homozygous recessive
pp = recessive color
The History of Heredity
Modern genetics begins with the work of Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk whose breeding experiments with garden peas led him to formulate the basic laws of heredity.
 In one experiment, Mendel cross-pollinated smooth yellow pea plants with wrinkly green peas.
In one experiment, Mendel cross-pollinated smooth yellow pea plants with wrinkly green peas. Mendel postulated that there are dominant and recessive traits in heredity.
In his experiment Mendel marked with capital letters dominant traits and with small letters recessive traits.
R = dominant round shape
r = recessive wrinkly shape
Heterozygous (Aa)
1 Parents Genes Aa
2 Parent Genes AA
Homozygous (AA) Result: All offspring's phenotype will have allergies. 2 offspring will be homozygous for the dominant trait Allergies, the other 2 heterozygous for allergies.
Homozygous alleles are purebred, HH, hh.
Heterozygous alles are hybrid, ex. Hh, Rr,
Trait
|
Phenotype - Physical appearance
|
Genotype - Genetic makeup
|
1. Hair color
|
brown, black, or red hair DOMINANT
|
LL or Ll
|
blond hair recessive
|
ll
|
|
2. Hair type
|
naturally curly DOMINANT
|
TT or Tt
|
naturally straight recessive
|
tt
|
|
3. Tongue curling
|
can curl tongue DOMINANT
|
CC or Cc
|
cannot curl tongue recessive
|
cc
|
|
4. Mid-digital hair
|
hair present, middle digit
of finger
|
MM or Mm
|
hair absent, middle digit of
finger
|
mm
|
|
5. Pigmented iris
|
eyes not blue
|
EE or Ee
|
blue eyes
|
ee
|
|
6. Widow's peak
|
peak in center of hairline
|
WW or Ww
|
no peak in center of
hairline
|
ww
|
|
7. Bent finger
|
little finger curves toward
others
|
BB or Bb
|
little finger straight
|
bb
|




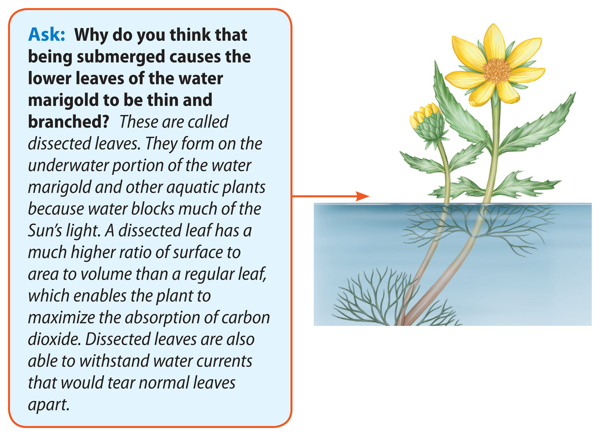
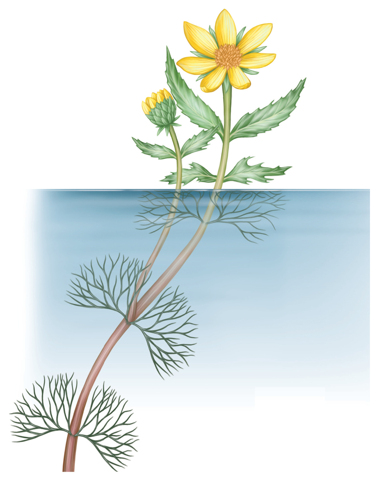
 Visual Check How might the ability to change color help an octopus survive in its environment?
Visual Check How might the ability to change color help an octopus survive in its environment?

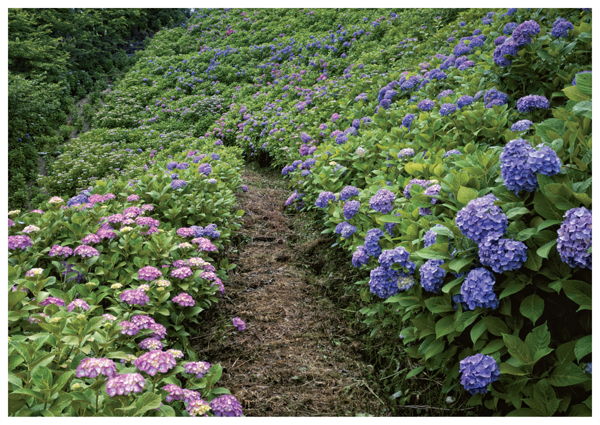
 Reading Check Does soil acidity affect genotype, phenotype, or both in hydrangeas?
Reading Check Does soil acidity affect genotype, phenotype, or both in hydrangeas?