Control and Coordination - Our Neurons
LinksHuman Body Systems Song
Click here for the Powerpoint
The Brain Videos...Watch them all! Nervous System Song Video on Neurons
Bill Nye on the Brain human nervous system
Watch a video here Synapse Video Here
LinksHuman Body Systems Song
Click here for the Powerpoint
The Brain Videos...Watch them all! Nervous System Song Video on Neurons
Bill Nye on the Brain human nervous system
Watch a video here Synapse Video Here
How does the nervous system interact with other body systems? Click here!
Fight or Flight Responses Auditory Illusions Optical Illusions 1 Optical Illusions 2 Optical Illusions 3 Auditory Illusions The Endocrine System Endocrine2 How the ear works
Optical Illusions 4 The incredible human machine
The nervous system, shown in Figure 3, and the endocrine system, which you will read about later, receive and process information about your internal and external environments. These two systems control many functions, including movement, communication, and growth, by working with other systems in the body and help maintain homeostasis.
Fight or Flight Responses Auditory Illusions Optical Illusions 1 Optical Illusions 2 Optical Illusions 3 Auditory Illusions The Endocrine System Endocrine2 How the ear works
Optical Illusions 4 The incredible human machine
The nervous system, shown in Figure 3, and the endocrine system, which you will read about later, receive and process information about your internal and external environments. These two systems control many functions, including movement, communication, and growth, by working with other systems in the body and help maintain homeostasis.
1. Key Concept Check How does the body respond to changes in its environment?
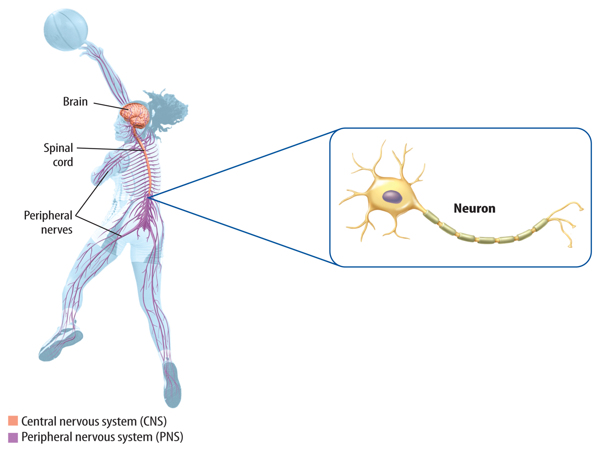
Figure 3 The brain and the spinal cord form the central nervous system. All other nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system that extends throughout the entire body.
The Nervous System
The nervous system is a group of organs and specialized cells that detect, process, and respond to information. The nervous system constantly receives information from your external environment and from inside your body. It can receive information, process it, and produce a response in less than 1 second.
Nerve cells, or neurons, are the basic units of the nervous system. Neurons can be many different lengths. In adults, some neurons are more than 1 m long. This is about as long as the distance between a toe and the spinal cord.
The nervous system includes the brain, the spinal cord, and nerves. The brain and the spinal cord form the central nervous system. Nerves outside the brain and the spinal cord make up the peripheral nervous system.
Processing Information The central nervous system is protected by the skeletal system. Muscles and other organs surround the peripheral nervous system. Information enters the nervous system through neurons in the peripheral nervous system. Most of the information then is sent to the central nervous system for processing. After the central nervous system processes information, it signals the peripheral nervous system to respond.
Voluntary and Involuntary Control The body carries out many functions that depend on the nervous system. Some of these functions such as breathing and digestion are automatic, or involuntary. They do not require you to think about them to make them happen. The nervous system automatically controls these functions and maintains homeostasis.
Most of the other functions of the nervous system are not automatic. They require you to think about them to make them happen. Tasks such as reading, talking, and walking are voluntary. These tasks require input, processing, and a response.
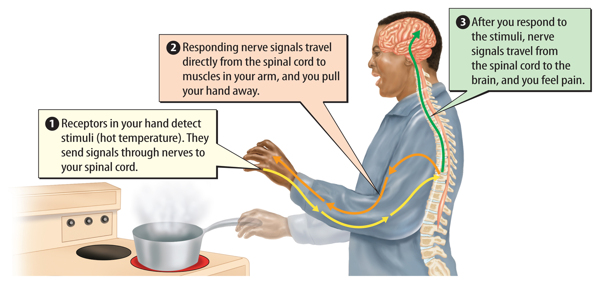
Reflexes Have you ever touched a hot pan with your hand? Touching a hot object sends a rapid signal that your hand is in pain. The signal is so fast that you do not think about moving your hand; it just happens automatically. Automatic movements in response to a signal are called reflexes. The spinal cord receives and processes reflex signals, as shown in Figure 4. Processing the information in the spinal cord instead of the brain helps the body respond more quickly.
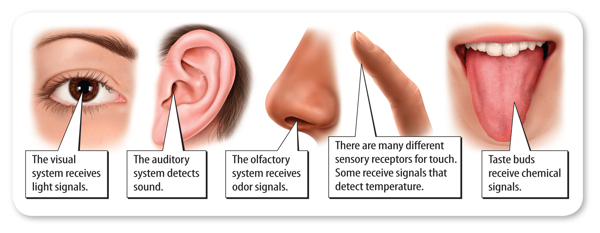
The Senses Humans detect their external environment with five senses—vision, hearing, smell, touch, and taste—as shown in Figure 5. Each of the five senses has specific neurons that receive signals from the environment. Information detected by the senses is sent to the spinal cord and then to the brain for processing and a response. Responses depend on the specific signal detected. Some responses cause muscles to contract and move such as when you touch a hot surface. The aroma of baking cookies might cause your mouth to produce saliva.
The Endocrine System
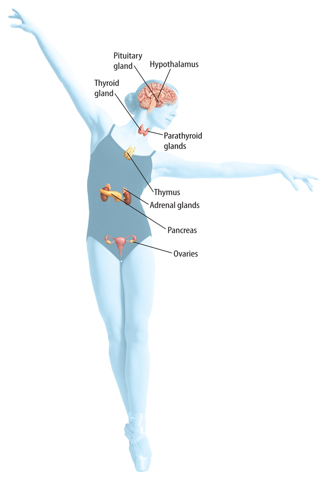
How tall were you in first grade? How tall are you now? From the time you were born until now, your body has changed. These changes are controlled by the endocrine system, shown in Figure 6. Like the nervous system, the endocrine system sends signals to the body. Chemical signals released by the organs of the endocrine system are called hormones. Hormones cause organ systems to carry out specific functions.
Why does your body need two organ systems to process information? The signals sent by the nervous system travel quickly through neurons. Hormones travel in blood through blood vessels in the circulatory system. These messages travel more slowly than nerve messages. A signal sent by the nervous system can travel from your head to your toes in less than 1 s, but a hormone will take about 20 s to make the trip. Although hormones take longer to reach their target organ system, their effects usually last longer.
Many of the hormones made by the endocrine system work with other organ systems and maintain homeostasis. For example, parathyroid hormone works with the skeletal system and controls calcium storage. Insulin is a hormone that is released from the pancreas that signals the digestive system to control nutrient homeostasis. Other hormones, such as growth hormone, work with many organ systems to help you grow.
2.  Reading Check How do hormones help the body maintain homeostasis?
Reading Check How do hormones help the body maintain homeostasis?
 Reading Check How do hormones help the body maintain homeostasis?
Reading Check How do hormones help the body maintain homeostasis?
Figure 6 The endocrine system uses hormones to communicate with other organ systems.
Lesson Assessment
Use Vocabulary
1. Distinguish between compact bone and spongy bone.
2. A chemical signal that is released by the endocrine system is a(n) __________.
3. Use the term neuron in a sentence.
Understand Key Concepts
4. An automatic movement in response to a signal is called a
A.hormone.
B.muscle.
C.neuron.
D.reflex.
5. Compare the role of tendons in helping the skeletal system and the muscular system work together
to a bridge between two cities.
to a bridge between two cities.
6. Infer How does the skeletal system protect other organ systems in the body?
7. Which part of the nervous system is shown below?
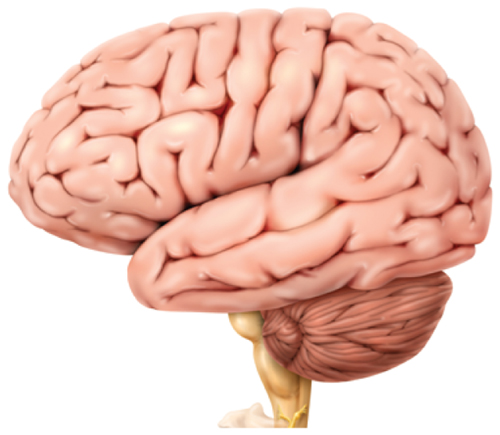

A.brain
B.neuron
C.peripheral nerve
D.spinal cord
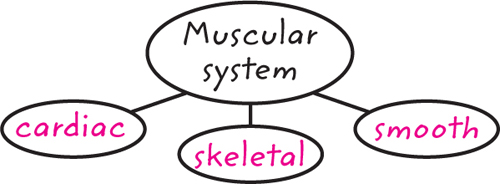
8. Which is NOT a type of muscle tissue?
A.cardiac
B.lymphatic
C.skeletal
D.smooth
9. Which is a part of the skeletal system?
A.ligament
B.spleen
C.thymus
D.trachea
Interpret Graphics
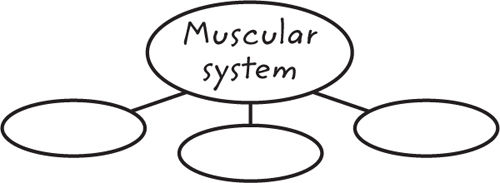
10. Summarize Copy and fill in the graphic organizer below to show the three types of muscle tissue.

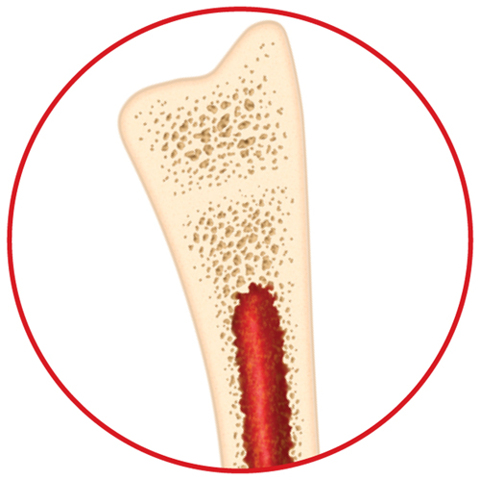
11. Predict the effect of having less compact bone than normal on the strength of the skeletal system by examining the figure below.

Critical Thinking
12. Hypothesize What would be the effect of losing one’s sight on the ability to digest food? Explain your answer.
13. Hypothesize how an injury to the spinal cord might affect the ability of the nervous system to sense and respond to a change in the environment.
14. Assess how the nervous system helps the muscular system control heart rate, digestion, and respiration.
15. Assess the role of the skeletal system in the storage of nutrients.
16. Name two hormones produced by the endocrine system and describe how they work with other organ systems and maintain homeostasis.
17. Identify the main functions of the skeletal, muscular, nervous, and endocrine systems.
Can you say the color name not read the word?

That's all for now....
Can you say the color name not read the word?
That's all for now....
Mrs. Sandoval

0 comments:
Post a Comment