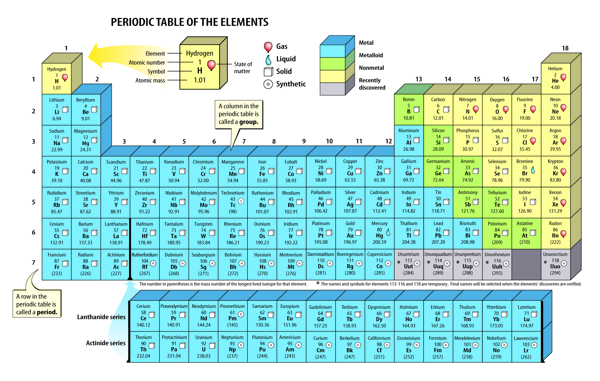
Scientists use a table called the periodic (pihr ee AH dihk) table to organize elements. The periodic table is a chart of the elements arranged into rows and columns according to their physical and chemical properties. It can be used to determine the relationships among the elements.
Today’s Periodic Table
You can identify many of the properties of an element from its placement on the periodic table. The table, as shown in Figure 4, is organized into columns, rows, and blocks, which are based on certain patterns of properties.
Figure 4 The periodic table is used to organize elements according to increasing atomic number and properties.
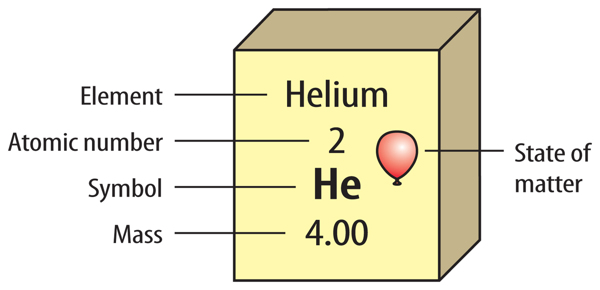
What is on an element key?
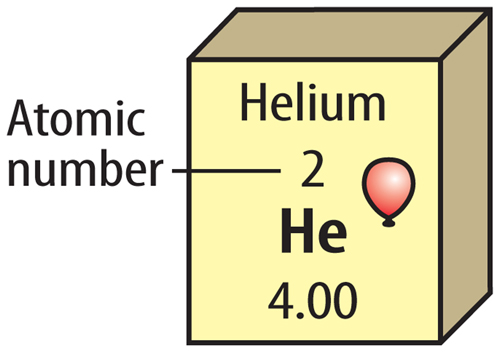
The element key shows an element’s chemical symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass. The key also contains a symbol that shows the state of matter at room temperature. Look at the element key for helium in Figure 5. Helium is a gas at room temperature. Some versions of the periodic table give additional information, such as density, conductivity, or melting point.
Figure 5 An element key shows important information about each element.
 Visual Check What does this key tell you about helium?
Visual Check What does this key tell you about helium?
Groups
A group is a column on the periodic table. Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties and react with other elements in similar ways. There are patterns in the physical properties of a group such as density, melting point, and boiling point. The groups are numbered 1–18, as shown in Figure 4.
1. Key Concept Check What can you infer about the properties of two elements in the same group?
Periods
The rows on the periodic table are called periods. The atomic number of each element increases by one as you read from left to right across each period. The physical and chemical properties of the elements also change as you move left to right across a period.
Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids
Almost three-fourths of the elements on the periodic table are metals. Metals are on the left side and in the middle of the table. Individual metals have some properties that differ, but all metals are shiny and conduct thermal energy and electricity.
With the exception of hydrogen, nonmetals are located on the right side of the periodic table. The properties of nonmetals differ from the properties of metals. Many nonmetals are gases, and they do not conduct thermal energy or electricity.
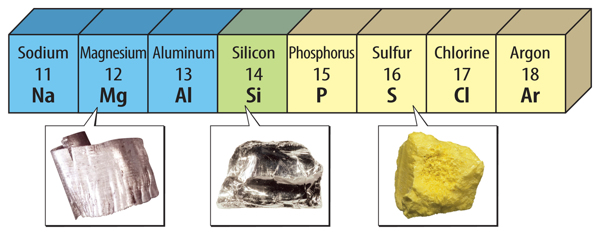
Between the metals and the nonmetals on the periodic table are the metalloids. Metalloids have properties of both metals and nonmetals. Figure 6 shows an example of a metal, a metalloid, and a nonmetal.
Figure 6 In period 3, magnesium is a metal, silicon is a metalloid, and sulfur is a nonmetal.
How Scientists Use the Periodic Table
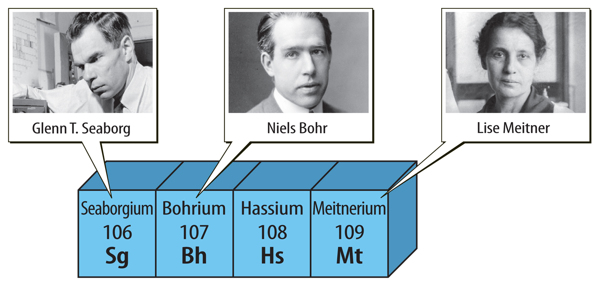
Even today, new elements are created in laboratories, named, and added to the present-day periodic table. Four of these elements are shown in Figure 7. These elements are all synthetic, or made by people, and do not occur naturally on Earth. Sometimes scientists can create only a few atoms of a new element. Yet scientists can use the periodic table to predict the properties of new elements they create. Look back at the periodic table in Figure 4.
What group would you predict to contain element 117? You would probably expect element 117 to be in group 17 and to have similar properties to other elements in the group. Scientists hope to one day synthesize element 117.
The periodic table contains more than 100 elements. Each element has unique properties that differ from the properties of other elements. But each element also shares similar properties with nearby elements. The periodic table shows how elements relate to each other and fit together into one organized chart. Scientists use the periodic table to understand and predict elements’ properties. You can, too.
1.  Reading Check How is the periodic table used to predict the properties of an element?
Reading Check How is the periodic table used to predict the properties of an element?
 Reading Check How is the periodic table used to predict the properties of an element?
Reading Check How is the periodic table used to predict the properties of an element?
Figure 7 Three of these synthetic elements are named to honor important scientists.
Lesson Review
Visual Summary
On the periodic table, elements are arranged according to increasing atomic number and similar properties.
A column of the periodic table is called a group. Elements in the same group have similar properties.
A row of the periodic table is called a period. Properties of elements repeat in the same pattern from left to right across each period.
Use Vocabulary
1. Identify the scientific term used for rows on the periodic table.
2. Name the scientific term used for columns on the periodic table.
Understand Key Concepts
3. The _________ increases by one for each element as you move left to right across a period.
4. What does the decimal number in an element key represent?
A. atomic mass
B. atomic number
C. chemical symbol
D. state of matter
5. What determines the order of elements on today’s periodic table?
A. increasing atomic mass
B. decreasing atomic mass
C. increasing atomic number
D. decreasing atomic number
6. The element key for nitrogen is shown below.
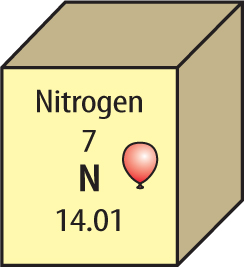
From this key, determine the atomic mass of nitrogen.

From this key, determine the atomic mass of nitrogen.
A. 7
B. 7.01
C. 14.01
D. 21.01
7. Look at the periodic table in the lesson. Which of the following lists of elements forms a group on the periodic table?
A. Li, Be, B, C, N, O, F, and Ne
B. He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, and Rn
C. B, Si, As, Te, and At
D. Sc, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Cu, Ni, and Zn
8. The following table lists some information about certain elements in group 17.
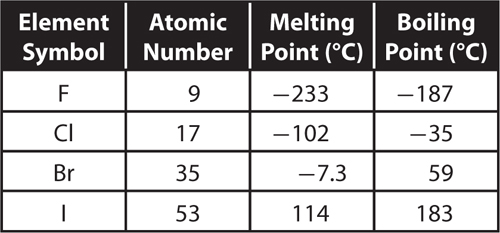
Which statement describes what happens to these elements as atomic number increases?

Which statement describes what happens to these elements as atomic number increases?
A. Both melting point and boiling point decrease.
B. Melting point increases and boiling point decreases.
C. Melting point decreases and boiling point increases.
D. Both melting point and boiling point increase.
Interpret Graphics
9. Classify each marked element, 1 and 2, as a metal, a nonmetal, or a metalloid.
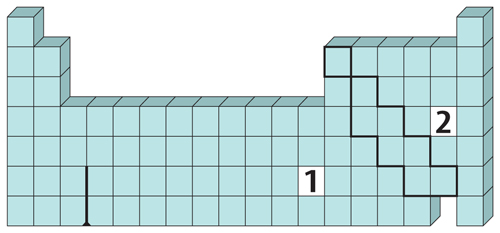

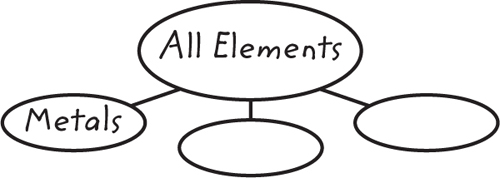
10. Identify Copy and fill in the graphic organizer below to identify the color-coded regions of the periodic table.

Critical Thinking
11. Predict Look at the perioidic table and predict three elements that have lower melting points than calcium (Ca).
12. The figure below shows a pattern of densities.
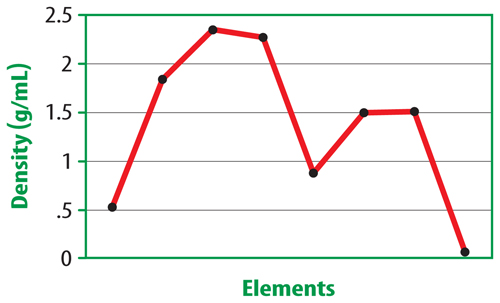
Infer whether you are looking at a graph of elements within a group or across a period.
Explain your answer.

Infer whether you are looking at a graph of elements within a group or across a period.
Explain your answer.
13. Explain how atomic number and properties are used to determine where element 115 is placed on the periodic table.
14. The photo below shows how the properties of materials determine their uses. How can the periodic table be used to help you find elements with properties similar to that of helium?


Nick Caloyianis/National Geographic/Getty Images
Math Skills: Use Geometry
15. Carbon (C) and silicon (Si) are in group 4 of the periodic table. The atomic radius of carbon is 77 pm and sulfur is 117 pm. What is the circumference of each atom?
16. The table below shows the atomic radii of three elements in group 1 on the periodic table.
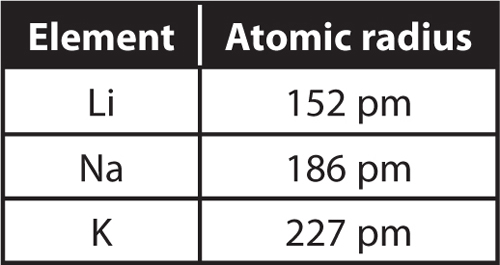

a. What is the circumference of each atom?
b. Rubidium (Rb) is the next element in Group 1.
What would you predict about the radius and circumference of a rubidium atom?
What would you predict about the radius and circumference of a rubidium atom?
0 comments:
Post a Comment